| |
Wounds that do not cause bleeding should be treated with as much and probably more attention than the wounds that do bleed. The danger here is that the damage cannot be clearly assessed. As a first aid administrator, you should be looking for signs of internal damage, like internal bleeding, internal tissue or organ damage, etc. For example, a blow to the head might not show any exterior signs of distress, not even a bruise, but the victim might be experiencing a life threatening condition because of internal bleeding. If misdiagnosed, the consequences can be catastrophic.
Below is the list of injuries where you should suspect internal injury:
- Car crashes, even when the impact/damage is minor
- Shock signs after the injury, even with no signs of any exterior damage
- Injury via collision, generally sustained in sports, especially if there is a loss
 of consciousness of consciousness
- Injury to abdominal or pain in abdominal
- Injury to the chest or pain in the chest
- Blood discharge after the injury
- Firearm or knife wounds
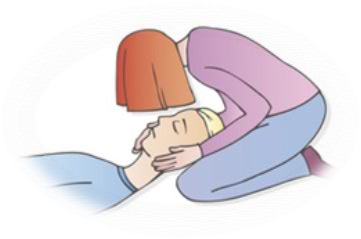
When faced with the victim that you suspect has a non-bleeding injury follow the following steps:
- Contact emergency services
- Put the victim in the horizontal position on his back
- Make sure the victim does not move
- Check for signs of shock
- If the victim does not respond, start CPR
 
|
|